Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall health, but sometimes life gets in the way, and dehydration sneaks up.
Whether it’s after an intense workout, a long day in the sun, or recovering from an illness, knowing how to hydrate fast can make all the difference.
Quick and effective hydration methods can help restore energy, improve focus, and support bodily functions.
In this article, readers will discover practical tips and scientifically-backed strategies to rehydrate quickly.
From the best beverages to drink to the role of electrolytes and hydration-boosting foods, these insights will ensure anyone can bounce back from dehydration in no time.

What Is Healthy Hydration?
Healthy hydration is crucial for optimal bodily function, supporting processes like temperature regulation and joint lubrication.
Regular fluid intake is necessary to replace water lost through sweat, urine, and breath. While the advice to drink eight glasses of water a day is a general guideline, individual needs vary based on factors like activity, climate, and diet.
Foods with high water content can also contribute to hydration. Maintaining electrolyte balance is important for muscle function, nerve communication, and overall hydration, with sports drinks and rehydration solutions being beneficial during intense activity or illness.
Monitoring urine color can help gauge hydration status, with pale yellow indicating adequate hydration.
5 Signs of Dehydration
Recognizing dehydration early helps in taking prompt corrective action. Here are five common signs to watch out for:
1. Xerostomia
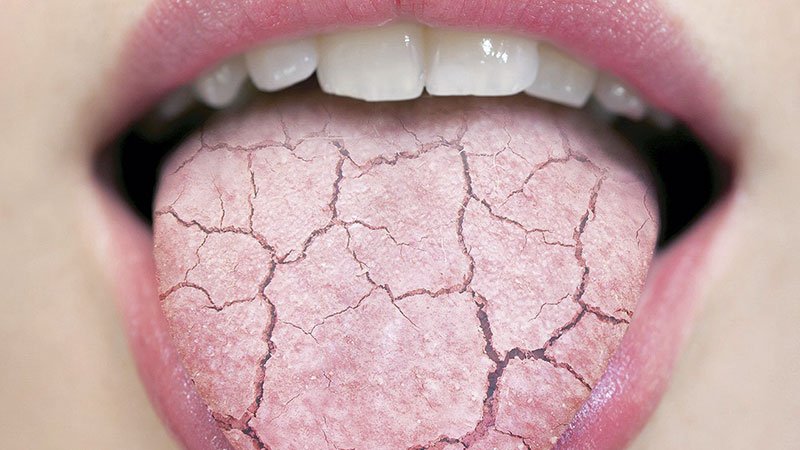
Xerostomia, or dry mouth, is often one of the first signs of dehydration. A lack of adequate saliva results in a sticky feeling in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and bad breath.
2. Headache
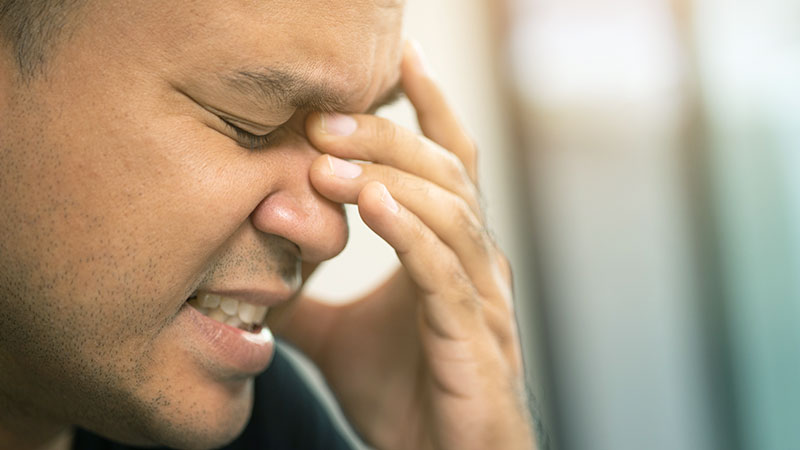

Headache is another common symptom of dehydration. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, blood volume decreases, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the brain, leading to discomfort or pain.
3. Dark Urine
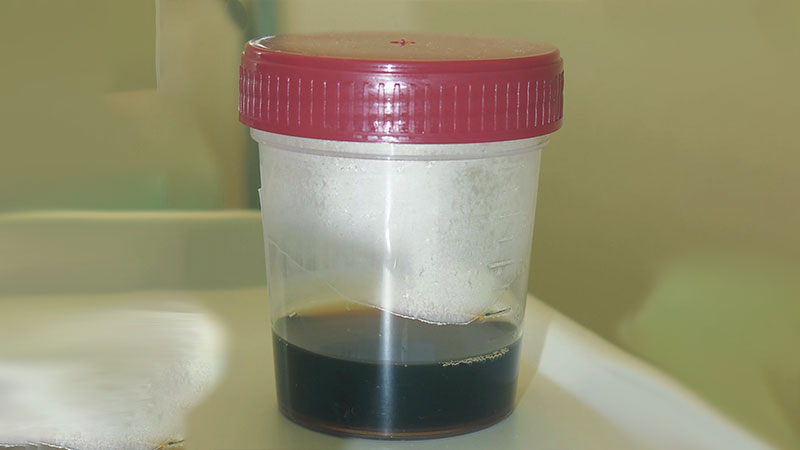

Dark urine signals dehydration. When the body doesn’t get enough fluids, urine becomes more concentrated, resulting in a darker color. Monitoring urine color provides a quick indicator of hydration status.
4. Thirst

Thirst is a clear and immediate sign of dehydration. As the body’s fluid levels drop, the sensation of thirst increases, prompting the individual to consume fluids to restore balance.
5. Dry Skin
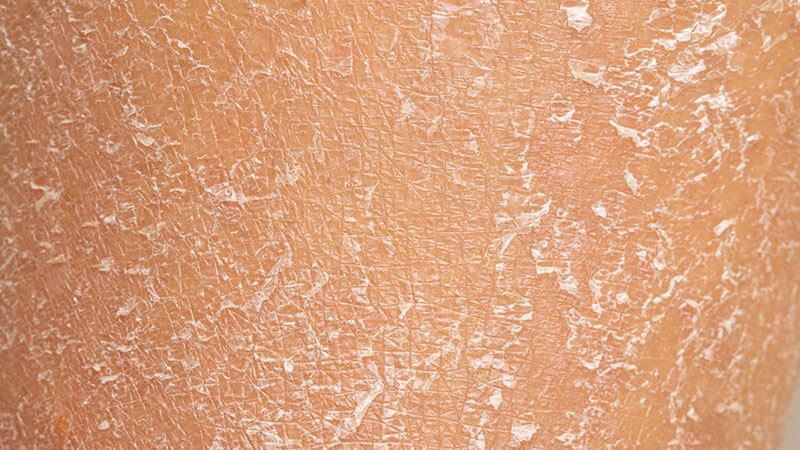
Dry skin is a less obvious but significant sign of dehydration. Lack of adequate hydration affects skin elasticity and moisture, making it appear dry and flaky. In severe cases, skin might also feel cool to touch.
How to Hydrate Fast?
Effective hydration strategies involve quick fluid intake and maintaining adequate electrolyte balance.
Drink Water
The most straightforward way to hydrate quickly is to drink water. Aim for 8 ounces every 15 minutes during physical activities.
Consuming electrolytes enhances hydration. Sports drinks, coconut water, and oral rehydration solutions efficiently replenish lost minerals, aiding in faster recovery.
Sip Electrolyte-Rich Drinks
Electrolyte-rich drinks like sports beverages restore hydration by replenishing sodium, potassium, and other vital minerals. These drinks accelerate the rehydration process.
Eat Water-Rich Foods
Consume water-rich foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and strawberries. These options contain over 90% water, aiding in quick hydration.
Avoid Dehydrating Foods
Limit intake of dehydrating foods like salty snacks and processed meats. High sodium content can worsen dehydration.
Use a Hypotonic Solution
Hypotonic solutions, which have lower salt concentrations than blood, facilitate rapid water absorption. Use these solutions for efficient rehydration.
Eat Plenty of Vegetables
Vegetables like lettuce and spinach have high water content and essential nutrients. Incorporate them into meals for additional hydration.
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) combines salt, sugar, and water to treat dehydration effectively. WHO recommends ORT for rapid rehydration during illness.
Sports Drinks
Sports drinks, containing electrolytes and carbohydrates, replenish lost fluids and energy. Choose low-sugar options for a healthier rehydration method.
Coffee and Tea
Consume coffee or tea in moderation as they contain water but can have mild diuretic effects. Black or green tea can be a hydrating alternative.
Skim and Lowfat Milk
Skim and lowfat milk offer hydration with added benefits of protein and electrolytes. They serve as a suitable post-exercise rehydration option.
Try Carb Alternatives
Include carbohydrate alternatives like oats or quinoa, which assist in maintaining fluid balance and support sustained hydration.
How Long Does It Take to Rehydrate?

The time required to rehydrate depends on the severity of dehydration and the methods used. For mild issues, rehydration can begin in just a few minutes.
Hydration continues as fluids replace lost moisture, and individuals may feel better within a few hours. Fully recovering from more significant dehydration usually takes several hours to up to 36 hours. Severe dehydration might need hospital treatment for complete recovery.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
Proper hydration requires ongoing attention. Implementing these strategies can help maintain optimal fluid balance.
- Drink Water Regularly: Water intake is essential throughout the day. Aim to drink small amounts frequently to stay hydrated.
- Carry a Water Bottle: Always have a reusable water bottle. This encourages regular drinking and ensures easy access to water.
- Foods High in Water Content: Include hydrating foods (e.g., cucumbers, watermelon) in your diet. These foods provide an additional source of fluids.
- Drink Before You’re Thirsty: Start drinking fluids before feeling thirsty. Thirst indicates early dehydration, so preemptive hydration is crucial.
- Drink Extra in the Morning: Increase water intake in the morning. This helps compensate for fluid loss during sleep and kickstarts hydration.
- Check Your Urine: Monitor urine color. Pale yellow urine suggests adequate hydration, while dark urine indicates a need for more fluids.
- Use Hydration Reminders: Set reminders. Use apps or alarms to prompt regular drinking, especially during busy or active periods.
- Avoid Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption. Alcohol dehydrates the body, so moderating intake can help maintain fluid balance.
Conclusion
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall health and bodily functions. By recognizing the signs of dehydration and implementing effective hydration strategies, individuals can quickly and efficiently restore their fluid balance.
Incorporating water-rich foods, electrolyte beverages, and regular fluid intake into daily routines can significantly enhance hydration.
Monitoring urine color and setting reminders to drink water can help maintain optimal hydration levels. Remember to increase water intake during physical activities and in hot climates.
By following these tips, individuals can ensure they stay hydrated and support their body’s health and performance.
